In perfect competition a firm's price is equal to its...
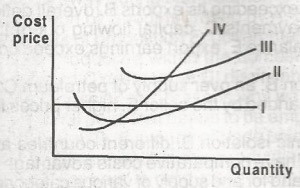
In perfect competition a firm's price is equal to its marginal revenue which is again equal to average revenue. This form maximizes its profits when its marginal cost (MC) is equal to price (p). Which of the curves in the diagram below represents the firm's marginal cost (MC)?
Curve I
Curve II
Curve III
Curve IV
Curves l and lll
Correct answer is D
No explanation has been provided for this answer.
Similar Questions
Which of the following is a threat to the existence of middlemen? ...
Robert T. Malthus postulated in his population theory that ...
The motive for holding money to meet unforeseen events is termed ...
A country whose economy is buoyant is likely to have ...
At the equilibrium price, quantity demanded is ...
The condition for equilibrium price and quantity under perfect competition is ...
The motive for holding money for investing in securities is referred to as ...
Product differentiation in monopolistic competition implies that ...