The figure above shows change in demand for commodity X which is a normal good. Use it to answer the questions that follows
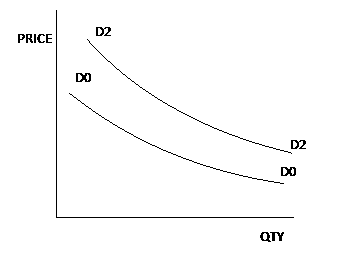
Which of the following caused the change in demand from D0 D0 to D2 D2?
Fall in income of consumer
Rise in the price of a substitute
Rise in the price of a complement
Fall in the supply of commodity X
Correct answer is B
A change in the demand from D0 D0 to D2 D2 is caused by the rise in the price of substitute, for example, if the price of milo increases, consumer will buy more of bournvita which will make the demand for bournvita to increase.
In order to increase revenue, government should tax commodities for which demand is
Perfectly price inelastic
Price inelastic
Price elastic
Unitary elastic
Correct answer is B
For government to generate more revenue, tax on commodities should be price inelastic. Inelastic means when tax is imposed, consumers do not react to tax i.e more of the goods are demanded.
What happens when the central bank increases the bank rate in an economy?
Borrowing is discouraged
Customers increase their borrowing
Banks can increase their lending
Money supply increases
Correct answer is A
Central bank discourage borrowing when bank rate is increased. Bank rate is one of the ways the central bank control money supply in an economy. If the bank rate is high, the supply of money will fall and vice versa.
Scale of preference
Opportunity cost
Complementary demand
Double coincidence of wants
Correct answer is D
Double coincidence of wants simply mean searching for those who need what you have and at the same time has what you need. It is a major barrier to barter trade.
Holding money to take care of contingencies is
A speculative motive
A transactions motive
A precautionary motive
An expansionary motive
Correct answer is C
A precautionary motive is when people hold money to meet unforseen contingencies or circumstances e.g accident, sickness etc. It varies inversely with the level of income.
JAMB Subjects
Aptitude Tests