7:5
5:7
1:2
2:1
Correct answer is C
Metals P, Q
original length lP, lQ
Increase in length ΔlP, ΔlQ
Linear expansivities αP, αQ
∴ αP/αQ = 2/3 ; and lP/lQ = 3/4
But increase in length, Δl = αlΔθ
∴ΔlP = αPlPΔθ
ΔlQ = αQlQΔθ
| ∴ | ΔlP | = | αPlPΔθ | = | 2 | x | 3 | = | 1 |
| ΔlQ | αQlQΔθ | 3 | 4 | 2 |
∴ Ratio of increase in length of P to Q = 1:2
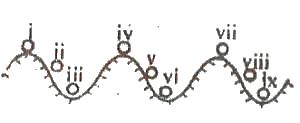
III, IV and VIII
II, V and VIII
III, VI and IX
I, IV and VII
Correct answer is C
A bod y is said to be in stable equilibrium if after a slight displacement, the body returns to its former position. Thus, position III, VI and XI represents position of stable equilibrium
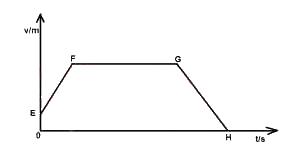
has no acceleration between point F and G
decelerates between F and H
has a constant soeed between points E and F
Accelerates between points F and G
Correct answer is A
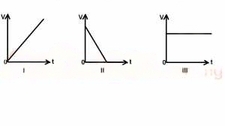
Above are the V-t graphs for
I Uniform acceleration
II uniform retardation
III Uniform velocity
Thus the car has no acceleration between point F and G since that portion of the graph represents uniform velocity
116.3 V
50.0 V
230.0 V
106.3 V
Correct answer is D
V = √ \({(v_l - v_c)}^2 + V^2R\)
V =√ \({(40 - 110)}^2 + 80^2\)
V = √ \({-70}^2 + 80^2\)
=√ 4900 + 6400
=√ 11300
= 106.3v
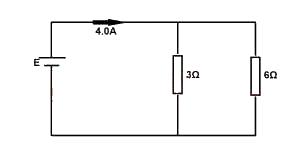
Calculate the e.m.f of the cell in the above circuit if its internal resistance is negligible
12 V
8 V
2 V
36 V
Correct answer is B
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 = 1/3 + 1/6
= 3/6
∴ R = 6/3 = 2
E = I(R + r) = 4(2 + 0) = 8v
JAMB Subjects
Aptitude Tests