2μC and 4μC
4μC and 2μC
100μC and 200μC
200μC and 100μC
Correct answer is C
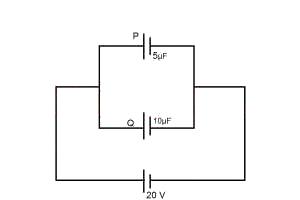
Since capacitance C = Q/V, => Q = CV
∴ Qp = 5 x 10-b x 20
= 100 x 10-b or 100μC
Qp = 10 x 10-b x 70
= 200 x 10-b or 200μC
Correct option 100μC and 200μC
5 ms-1
20 ms-1
30 ms-1
40 ms-1
Correct answer is B
For transverse wave on string
velocity V = √T/M
where T is the tension, and M is the mass per unit length
∴ for T = 12N and M = 3.0 x 10-2kgm-1
V=
√ 12 / (3.0x10-2
=
√ 12 / 0.03
=
√ 1200 / 3
=
√ 1200 / 3 = 20
∴V = 20m/s
y = 0.15 sin 200π(x - 5.5t)
y = 0.15 sin π(0.01x - 5.5t)
y = 0.15 sin 5.5π(x - 200t)
y = 0.15 sin π(550x - 0.01t)
Correct answer is A
The general wave equation is given by Y = sin A 2π/λ [x - vt]
= Sin A [(2π X)/λ - (2π vt)/λ]
thus if A = 0.15;λ = 0.01m; f = 550Hz
then V = f x λ = 550 x 0.01 = 5.50m/s
∴ Y = 0.15 sin [(2 x λ x X)/0.01 - (2 x λ x 5.5t)/0.01]
= 0.15 sin[200λX - 200 x λ x 5.5t]
∴ Y = 0.15 sin 200λ[x - 5.5t]
fo/2
2fo
fo/√2
fo√2
Correct answer is D
For a vibrating sonometer wire, the frequency
F = l/2l √(T/m)
and if the length, l and mass per unit length, m, are constant, then Fo ∝ √T => FoK√T or Fo/√T = K
=> F1o/√F1 = F2o/√F2
∴ F1o/√T1 = F2o/√T2
| thus F2 = | F3x√(2T1 |
| __√T1 |
=
| = | Fox√2 x √T1 |
| √T1 |
∴F2 = Fo x √2 = Fox√2
4.0 m
5.0 m
2.0 m
1.5 m
Correct answer is C
For a simple pendulum, the period T = 2π
√ 1/g
Since g, 2 and π are constant, => T ∝ √l
∴ T = K√l
Let the original length = l
thus for the length l, period T = 17s
∴ 17 = K√1 .................. [1]
Again, for the new length [1 - 1.5]
the period T = 8.5s
∴ 8.5 = k
√ [1-1.5] ...............[2]
thus dividing eqn [1] by eqn[2] we have
17/8.5 = √(l/l-1.5)
∴2 = √(l/l-1.5)
=>4 = (l/l-1.5)
∴l = 4[l-1.5]
= 4l - 6.0
∴4l - l = 6.0
3l = 6.0
l = 2.0m
JAMB Subjects
Aptitude Tests