One of these is not an assumption of the cardinalist theory of utility?
The consumer is rational
Diminishing marginal utility
The concept of money utility
Consistency and transivity of choice
Correct answer is D
No explanation has been provided for this answer.
In the case of highly or close complementary goods, the indifference curve is______
A straight line
A right-angled
L-shaped
Curvature
Correct answer is D
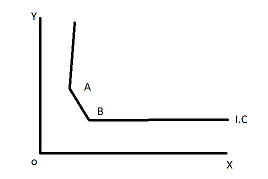
From the diagram, the shape is near the bend i.e Curvature at point A and point B (point of Origin).
The most important cost curve for the firm is_________
MC
AC
TC
FC
Correct answer is B
Average cost shows the cost per unit of any chosen output.
Economies of scale
Money cost
Opportunity cost
Cost functions
Correct answer is A
Economies of scale which is also known as scale of production set the size of plant, the number of plants installed and the technique of product. In the short-run, there is no time for the plant to expand while in the long-run, there is enough time for the firm to expand its size of plant which makes the AC α MC shape flatter.
Restrictive monetary policy is designed to curtail aggregate demand and to overcome________
Deflation
Reinflation
Disinflation
Inflationary gap
Correct answer is D
Restrictive monetary policy which is also known as contractionary monetary policy is used to increase interest rate and reduce investment so as to control inflation in an economy.
JAMB Subjects
Aptitude Tests