I only
I and II only
I, II, and III only
I and III
Correct answer is C
The kinetic-molecular theory of gases assumes that ideal gas molecules:
(1) are constantly moving;
(2) have negligible volume;
(3) have negligible intermolecular forces;
(4) undergo perfectly elastic collisions; and
(5) have an average kinetic energy proportional to the ideal gas's absolute temperature.
Kg m\(^{2}\) s\(^{-1}\)
Kg\(^{2}\) m s\(^{-2}\)
Kg m\(^{2}\) s\(^{-2}\)
Kg m s\(^{-1}\)
Correct answer is C
Joule as the unit of work done or energy used.
Force = mass × acceleration
Work = Force × Distance
Work = mass x acceleration x distance
Joule = kg × \(\frac{m}{s^2}\) × m
→ kg m\(^2\) s\(^{-2}\)
s \(\alpha\) t\(^{-2}\)
s \(\alpha\) t\(^{-1}\)
s \(\alpha\) t
s \(\alpha\) t\(^{2}\)
Correct answer is D
Mathematically; S = vt + \(\frac{1}{2}\) at\(^2\)
: S ∝ t\(^2\)
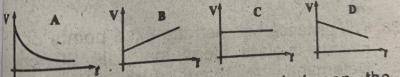
Which of the illustrated graphs above represents a body moving with uniform retardation?
A
B
C
D
Correct answer is D
If a body moves with uniform retardation, the velocity-time graph is a straight line.
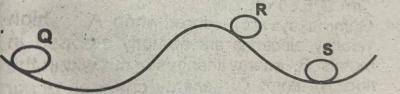
S only
Q only
R only
Q and S only
Correct answer is A
A system is in neutral equilibrium if its equilibrium is independent of displacements from its original position. A marble S on a flat horizontal surface is an example.
WAEC Subjects
Aptitude Tests