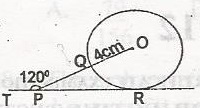
2.32cm
1.84cm
0.62cm
0.26cm
Correct answer is C
No explanation has been provided for this answer.
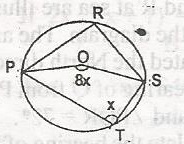
The diagram is a circle with centre P. PRST are points on the circle. Find the value of < PRS
144o
72o
40o
36o
Correct answer is A
Reflex < POS = 2x (angle at centre is twice that at circumference)
reflex < POS + < POS = 350o(angles at a point)
i.e. 2x + 8x = 360o
10x = 360o
x = \(\frac{360}{10}\)
= 36o
< PRS = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
< POS(< at centre twice that circumference)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 8x = 4x
4 x 36o
< PRS = 144
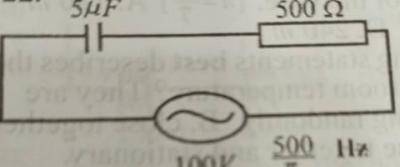
The diagram above is an illustration of an a.c. circuit.Calculate the reactance of the capacitor.
2016Ω
2000Ω
200Ω
4000Ω
Correct answer is C
Capacitive reactance, X\(_C\) = \(\frac{1}{2πFC}\) → \(\frac{1}{2π * 500/π * 5 * 10^{-6}}\)
= \(\frac{1}{0.005}\) → 200Ω
Which of the following statements is an effect of compressing gas molecules at constant temperature?
The pressure on the molecules decreases.
The molecules gain more kinetic energy
The molecules make more impact per second on the walls of the container
The molecules increase in size
Correct answer is C
More collisions mean more force, so the pressure will increase.
When the volume decreases, the pressure increases.
This shows that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
This is shown by Boyle's law.
A ball is swung in a horizontal circle of centre O with a constant speed. acceleration?
Away from O
Along the Circumference of the circle
Toward centre O
Along a tangent to the circle
Correct answer is C
Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is a special type of periodic motion where the restoring force on the moving object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the object's displacement and acts towards the object's equilibrium position.
WAEC Subjects
Aptitude Tests