Which of the following will increase the demand for labour?
Increase wage rate
Labour's demand for output
Low wage rate
Low marginal productivity
Correct answer is C
Factors that can shift the demand curve for labour include: a change in the quantity demanded of the product that the labour produces; a change in the production process that uses more or less labour; and a change in government policy that affects the quantity of labour that firms wish to hire at a given wage. When the payment for labour is low, fills will be willing to employ more people than with an increased wage rate.
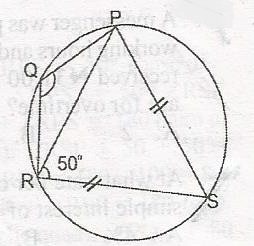
In the diagram, |SP| = |SR| and < PRS = 50o. Calculate < PQR
120o
110o
100o
80o
Correct answer is C
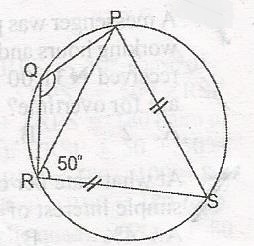
< PRS = RPS = 50o (base of isosceles)
RPS = 50o; < RSP + < PRS + < RPS = 180(sum of < s in a triangle)
< RPS + 50 + 50 = 180
< RSP = 180 - 100 = 80
then < PQR + < RSp = 180 (opp. < S of cyclic quad.)
< PQR + 80 = 180o
< PQR = 180 - 80
= 100
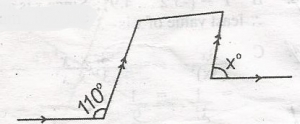
From the diagram, find the value of x in the diagram.
80o
70o
55o
35o
Correct answer is B
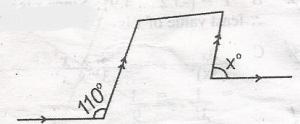
y + 110o = 180o(angles on a straight line)
y = 180 - 110
= 70o
x = y(corresponding angles)
x = 70o
Frictional unemployment occurs when?
There is a change in the technique of production
Job seekers lack information where jobs exist
Bad weather prevents work from progressing
Job seekers have disabilities
Correct answer is B
Frictional unemployment is a type of unemployment that arises when workers are searching for new jobs or are transitioning from one job to another
Frictional unemployment refers to people who are simply moving from one job to another, but are taking their time. It is part of the jobless total caused by individuals who are spending time searching for another job, or perhaps are taking a break before beginning with a new employer. Even in a country where there is technically full employment, there will always be some frictional employment, simply because employees change jobs occasionally.

24cm2
12cm2
10cm2
6cm2
Correct answer is B
Since tan y = \(\frac{2}{3}\) and LN = 4
tan y = \(\frac{2 \times 4}{3 \times 4} = \frac{8}{12} = \frac{4}{6}\)
then tan y = \(\frac{opp}{adj}\)
MN = 6cm
Area of angle LMN = \(\frac{1}{2}\)bh
= \(\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4\)
= 12cm3
WAEC Subjects
Aptitude Tests