Physics Questions and Answers
If you want to learn more about the nature and properties of matter and energy or you're simply preparing for a Physics exam, these Physics past questions and answers are ideal for you.

If you want to learn more about the nature and properties of matter and energy or you're simply preparing for a Physics exam, these Physics past questions and answers are ideal for you.
400 ms-1
4,000 ms-1
8,000 ms-1
160,000 ms-1
Correct answer is A
The velocity of sound in air, V∝√T, where T is absolute temperature
Thus V = K√T or K = V/T
V is independent of pressure and density at a fixed temperature.
∴ V1/√T1 = V2/√T2
T1 = 16 + 273 = 289K, V1 = 340ms-1
T2 = 127 + 273 = 400K, V2 = ?
| 340 | = | V2 |
| √289 | √400 |
| ∴ V2 = | 340√400 |
| _√289 |
= 400m/s
7:5
5:7
1:2
2:1
Correct answer is C
Metals P, Q
original length lP, lQ
Increase in length ΔlP, ΔlQ
Linear expansivities αP, αQ
∴ αP/αQ = 2/3 ; and lP/lQ = 3/4
But increase in length, Δl = αlΔθ
∴ΔlP = αPlPΔθ
ΔlQ = αQlQΔθ
| ∴ | ΔlP | = | αPlPΔθ | = | 2 | x | 3 | = | 1 |
| ΔlQ | αQlQΔθ | 3 | 4 | 2 |
∴ Ratio of increase in length of P to Q = 1:2
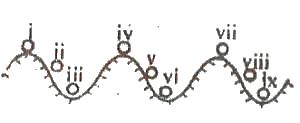
III, IV and VIII
II, V and VIII
III, VI and IX
I, IV and VII
Correct answer is C
A bod y is said to be in stable equilibrium if after a slight displacement, the body returns to its former position. Thus, position III, VI and XI represents position of stable equilibrium
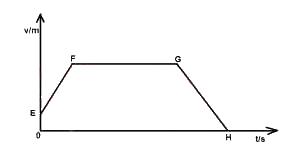
has no acceleration between point F and G
decelerates between F and H
has a constant soeed between points E and F
Accelerates between points F and G
Correct answer is A
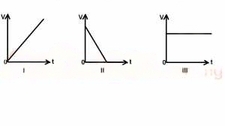
Above are the V-t graphs for
I Uniform acceleration
II uniform retardation
III Uniform velocity
Thus the car has no acceleration between point F and G since that portion of the graph represents uniform velocity
116.3 V
50.0 V
230.0 V
106.3 V
Correct answer is D
V = √ \({(v_l - v_c)}^2 + V^2R\)
V =√ \({(40 - 110)}^2 + 80^2\)
V = √ \({-70}^2 + 80^2\)
=√ 4900 + 6400
=√ 11300
= 106.3v