160o
140o
120o
100o
Correct answer is D
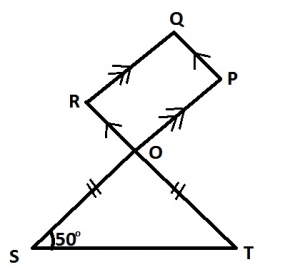
< T = < S = 50° (OS = OT)
< SOT = 180° - 2(50°) = 80°
< ROP = 80° (vertically opposite angle)
\(\therefore\) < OPQ = 180° - 80° = 100° (adjacent angles)
If the interior angles of hexagon are 107°, 2x°, 150°, 95°, (2x-15)° and 123°, find x.
\(57\frac{1}{2}^{\circ}\)
\(65^{\circ}\)
\(106^{\circ}\)
\(120^{\circ}\)
Correct answer is B
Sum of interior angle in a hexagon = (6 - 2) x 180°
= 720°
\(\therefore\) 107° + 2x° + 150° + 95° + (2x - 15)° + 123° = 720°
460 + 4x = 720 \(\implies\) 4x = 720 - 460
4x = 260° \(\implies\) x = 65°
75o
150o
160o
68o
Correct answer is B
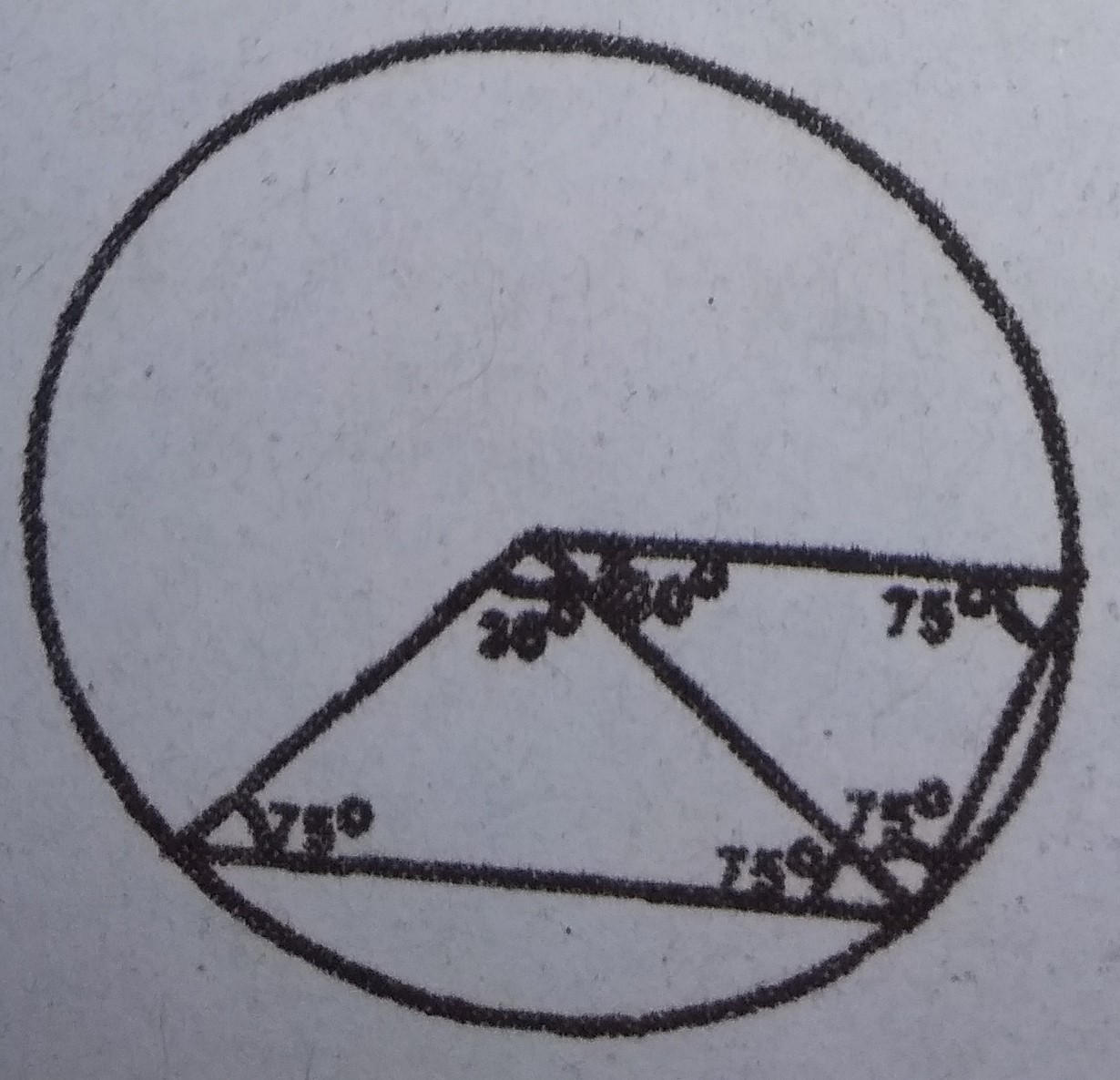
Interior angle = 2(75°)
= 150°
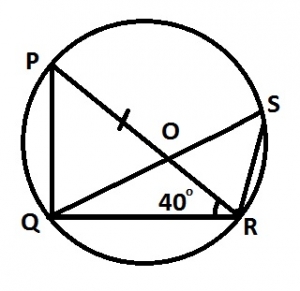
In the diagram, PQRS is a circle center O. PQR is a diameter and ∠PRQ = 40°. Calculate ∠QSR
30o
40o
45o
50o
Correct answer is D
< Q = < R (OQ = OR = radii)
< QOR = 180° - 2(40°) = 100°
< QSR = < RPQ = \(\frac{1}{2}\) < QOR
= \(\frac{100}{2} = 50°\)
I and II only
III only
II only
II and III only
Correct answer is B
No explanation has been provided for this answer.
WAEC Subjects
Aptitude Tests