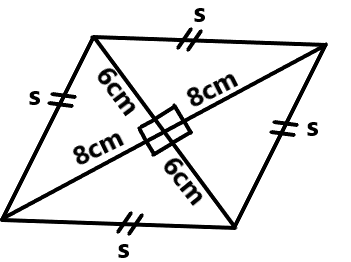
Mathematics Questions and Answers
How good are you with figures and formulas? Find out with these Mathematics past questions and answers. This Test is useful for both job aptitude test candidates and students preparing for JAMB, WAEC, NECO or Post UTME.