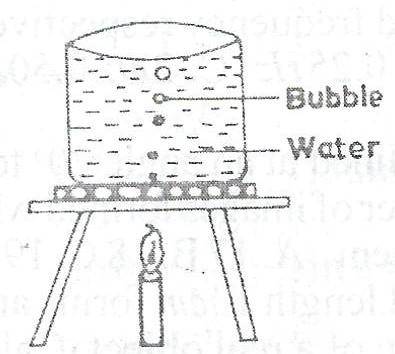
water pressure on the bubbles decreases
density of water increases with rise in temperature
volume of water increases with rise in temperature
atmospheric pressure on the bubbles decreases
Correct answer is A
When a bubble is deep under water, it has both atmospheric pressure and water pressure (giving it depth), acting on it but as it rises, the water pressure decreases. At this point, the basic pressre acting on the bubble is the atmospheric pressure. Recall that pressure is inversely proportional to volume (Boyles' law), hence, the less the pressure, the more the volume
A plane is inclined at an angle \(\theta\) to the horizontal. Its velocity ratio is
\(sin\theta\)
\(tan\theta\)
\(\frac{1}{sin\theta}\)
\(\frac{1}{tan\theta}\)
Correct answer is C
Velocity ratio = \(\frac{Effort distance}{Load distance}\)
On an inclined plane, it is the inverse of \(sin\theta\) = \(\frac{1}{sin\theta}\)
2400J
6800J
7251J
24000J
Correct answer is D
The quantity of heat needed to melt ice = mL (where m is the mass of ice and L is the specific latent heat of fusion of ice)
Q = \(50 \times 336 = 16800J\) but this is 70% of the total heat supplied so that we have,
70% total heat = 16800J
\(\frac{70}{100}\) of total heat = 16800J
⇒ Total heat supplied = \(\frac{16800\times100}{70} = 24000J\)
The energy stored in a spring of stiffness constant k = 2000\(Nm^{-1}\) when extended 4cm is
0.16J
1.60J
16.00J
160.00J
Correct answer is B
The spring constant = the measure of stiffness = 2000\(Nm^{-1}\)
Energy stored in a spring = Work done to stretch it through a distance = change in potential energy
= \(\frac{kx^{2}}{2}\) = \(\frac{2000 \times (0.04)^{2}}{2}\) (converting 4cm to metres)
= \(\frac{3.2}{2} = 1.60J\)
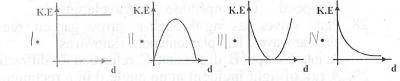
I
II
III
IV
Correct answer is B
No explanation has been provided for this answer.
WAEC Subjects
Aptitude Tests