An example of a mechanical wave is---------
water waves
radio waves
x-rays
light rays
Correct answer is A
A mechanical wave is a wave that is an oscillation of matter.
A sound wave is a mechanical wave that propagates along or through a medium by particle-to-particle interaction.
Sound waves, water waves and seismic waves are some examples of mechanical waves mechanical wave.
I. The average speed of the molecules increases
II. The temperature of the gas increases
III. The molecules hit the walls of the container more often than before the compression
I only
I and II only
I, II, and III only
I and III
Correct answer is C
The kinetic-molecular theory of gases assumes that ideal gas molecules:
(1) are constantly moving;
(2) have negligible volume;
(3) have negligible intermolecular forces;
(4) undergo perfectly elastic collisions; and
(5) have an average kinetic energy proportional to the ideal gas's absolute temperature.
Kg m\(^{2}\) s\(^{-1}\)
Kg\(^{2}\) m s\(^{-2}\)
Kg m\(^{2}\) s\(^{-2}\)
Kg m s\(^{-1}\)
Correct answer is C
Joule as the unit of work done or energy used.
Force = mass × acceleration
Work = Force × Distance
Work = mass x acceleration x distance
Joule = kg × \(\frac{m}{s^2}\) × m
→ kg m\(^2\) s\(^{-2}\)
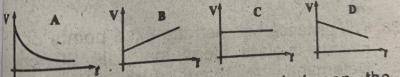
Which of the illustrated graphs above represents a body moving with uniform retardation?
A
B
C
D
Correct answer is D
If a body moves with uniform retardation, the velocity-time graph is a straight line.
\(\gamma\)=a
\(\gamma\)=3\(\alpha\)
\(\gamma\)=2a
\(\gamma\)=\(\frac{1}{3} \alpha \)
Correct answer is B
cubic and linear expansivity are related by this equation. γ=3α.
The area under a force-time graph represents--------
change in kinetic energy
change in momentum
change in work done
change in internal energy
Correct answer is B
It is a graph that represents the force that acts on a body in a certain amount of time.
Force on the object is represented by the y-axis and time taken by the object is represented by the y axis.
The area under the curve indicates the impulse, the change in momentum that the object undergoes.
WAEC Subjects
Aptitude Tests
Latest Jobs
Information and Communication Manager at Nigerian Breweries Plc
Area Sales Manager at Airtel Nigeria
State Business Manager at Airtel Nigeria
Regional Technical Officer at Airtel Nigeria
Business Manager at Airtel Nigeria
Contract Administrator at Robert Walters
Import & Export Manager at Kerildbert Holdings Limited
JV Account Payable Officer at WTS Energy