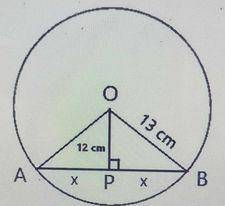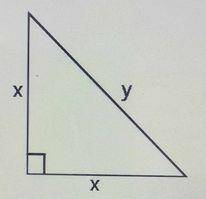
Perimeter of a triangle = sum of all sides
⇒ \(P = y + x + x = 2\)
⇒ \(y + 2x = 2\)
⇒ \(y= 2 - 2x\)-----(i)
Using Pythagoras theorem
\(y^2 = x^2 + x^2\)
⇒ \(y^2 = 2x^2\)
⇒ \(y = \sqrt2x^2\)
⇒ \(y = x\sqrt2\)-----(ii)
Equate \(y\)
⇒ \(2 - 2x = x\sqrt2\)
Square both sides
⇒ \((2 -2x) ^2 = (x\sqrt2)^2\)
⇒ \(4 - 8x + 4x^2 = 2x^2\)
⇒ \(4 - 8x + 4x^2 - 2x^2 = 0\)
⇒ \(2x^2 - 8x + 4 = 0\)
⇒ \(x = \frac{-(-8)\pm\sqrt(-8)^2 - 4\times2\times4}{2\times2}\)
⇒ \(x = \frac{8\pm\sqrt32}{4}\)
⇒ \(x = \frac{8\pm4\sqrt2}{4}\)
⇒ \(x = 2\pm\sqrt2\)
⇒ \(x = 2 + \sqrt2\) or \(2 - \sqrt2\)
∴ \(x = 2 - \sqrt2\) (for \(x\) has to be less than its perimeter)
∴ \(y = 2 - 2x = 2 - 2(2 - \sqrt2) = -2 + 2 \sqrt2\)
∴ The length of the longer side = -2 + 2\(\sqrt2\)m